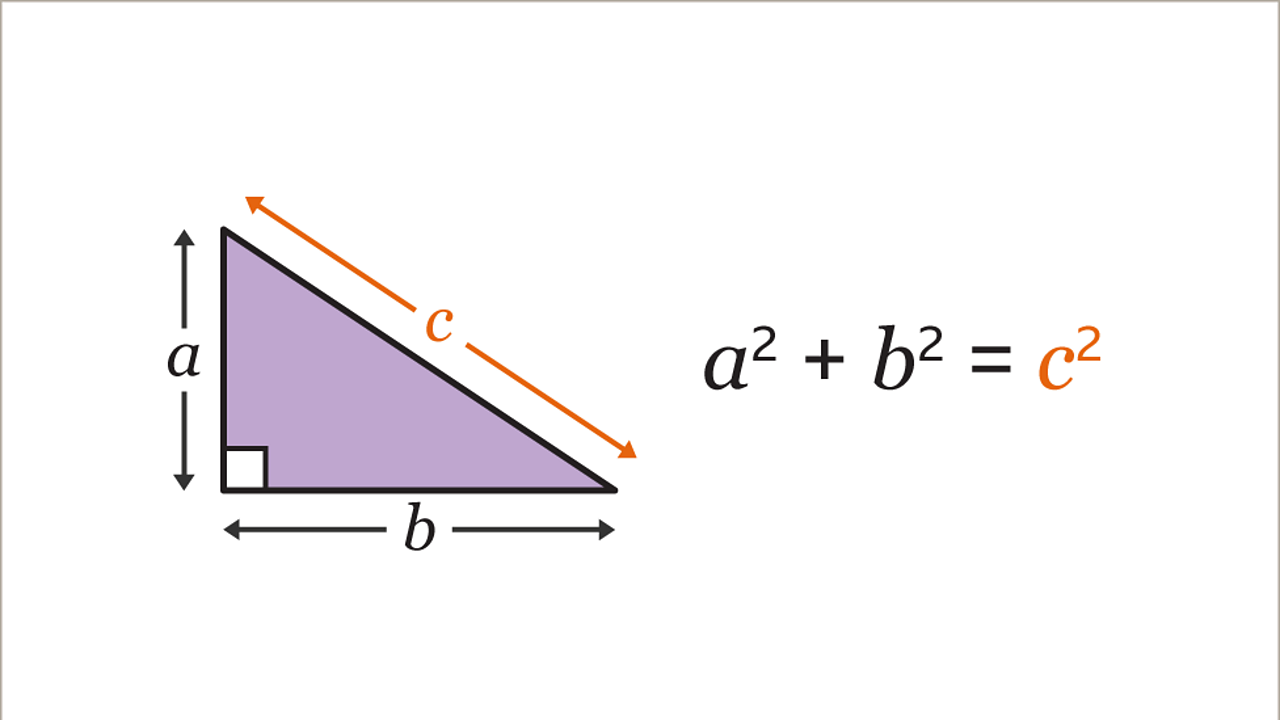Pythagoras
The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right-angled
triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse
(c) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths
of the other two sides (a and b).
Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
c*2 = a*2 + b*2
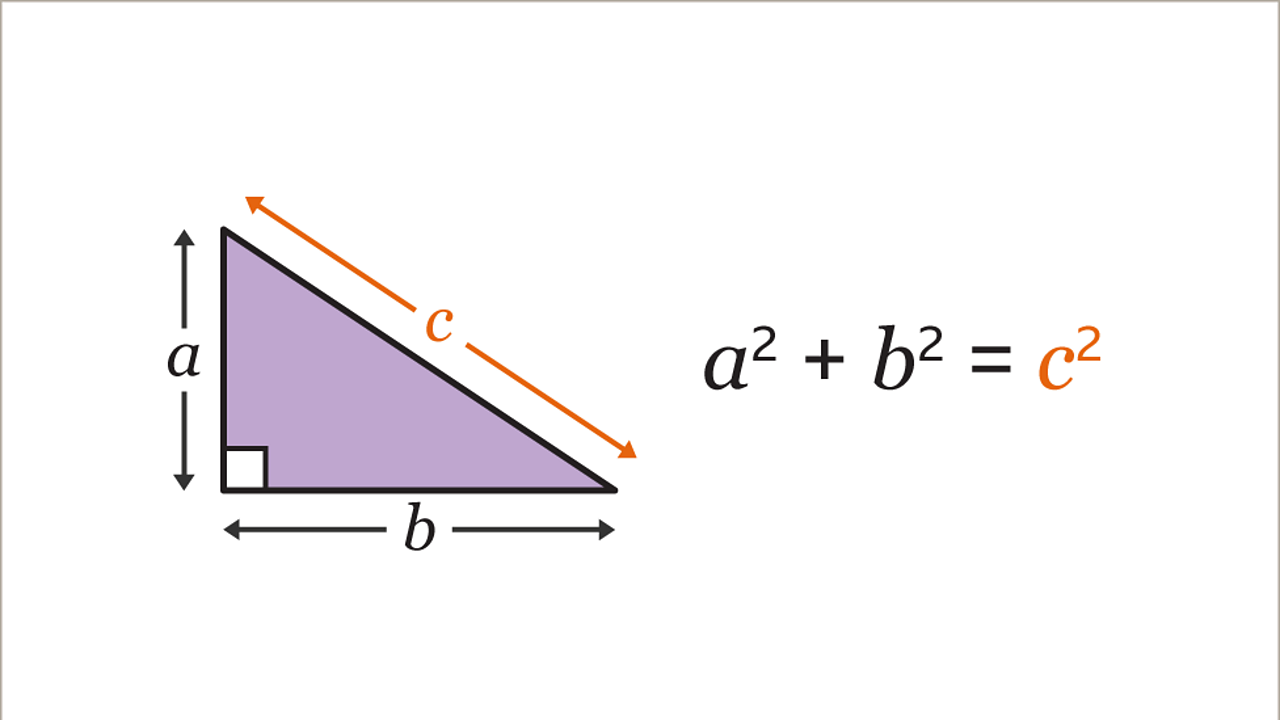
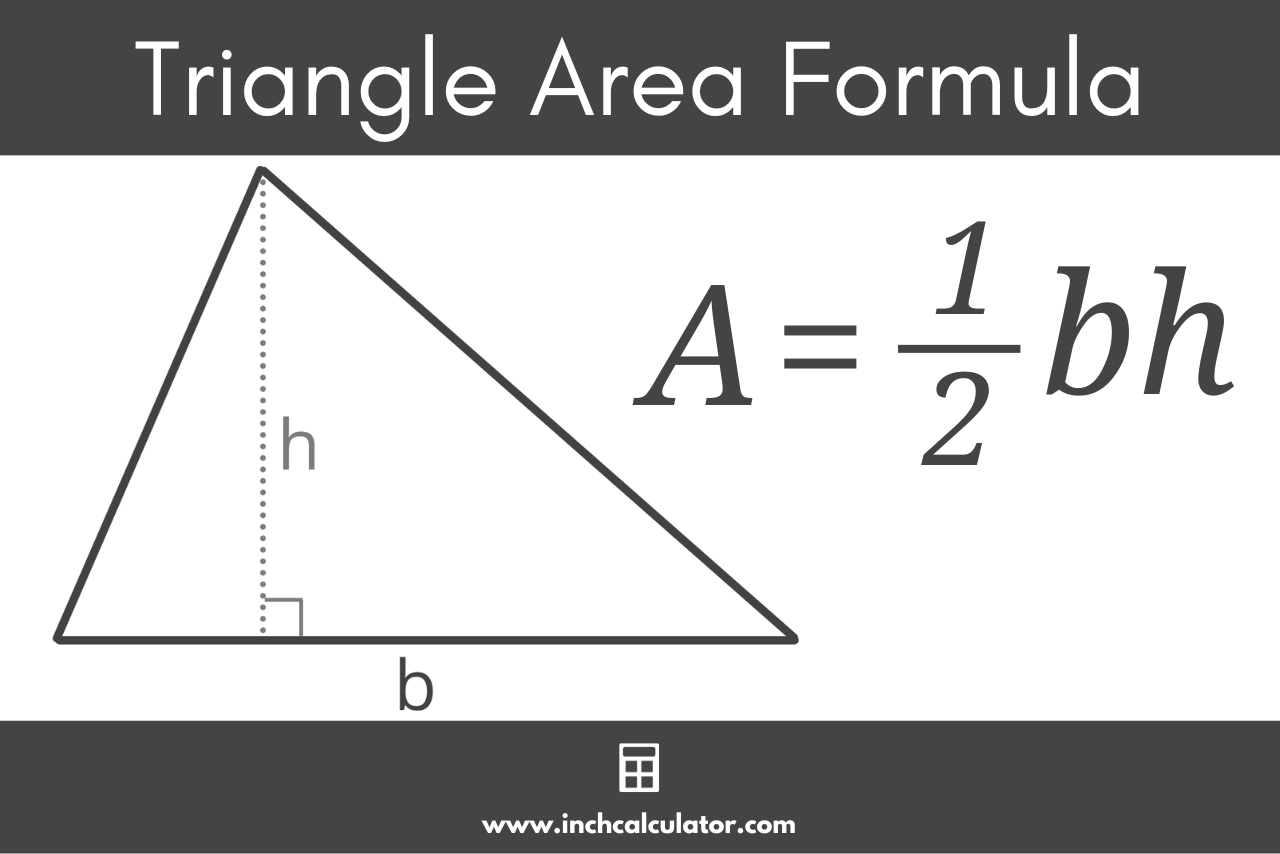
Triangle Area
The area of a triangle is calculated using the
formula: A = 1/2 * base * height,
where the base is one side of the triangle, and the height is the
perpendicular distance from the base to the opposite vertex.
It's a simple and elegant way to quantify the space enclosed
by the three sides of a triangle, capturing the essence of its
geometric presence.
Rectangle Area
The area of a rectangle is found by multiplying its length
and width. The formula is A = length × width. This
straightforward calculation unveils the extent of the
two-dimensional space enclosed by the four right angles
of a rectangle.
It's a concise and effective way to quantify
the geometric territory defined by its sides.
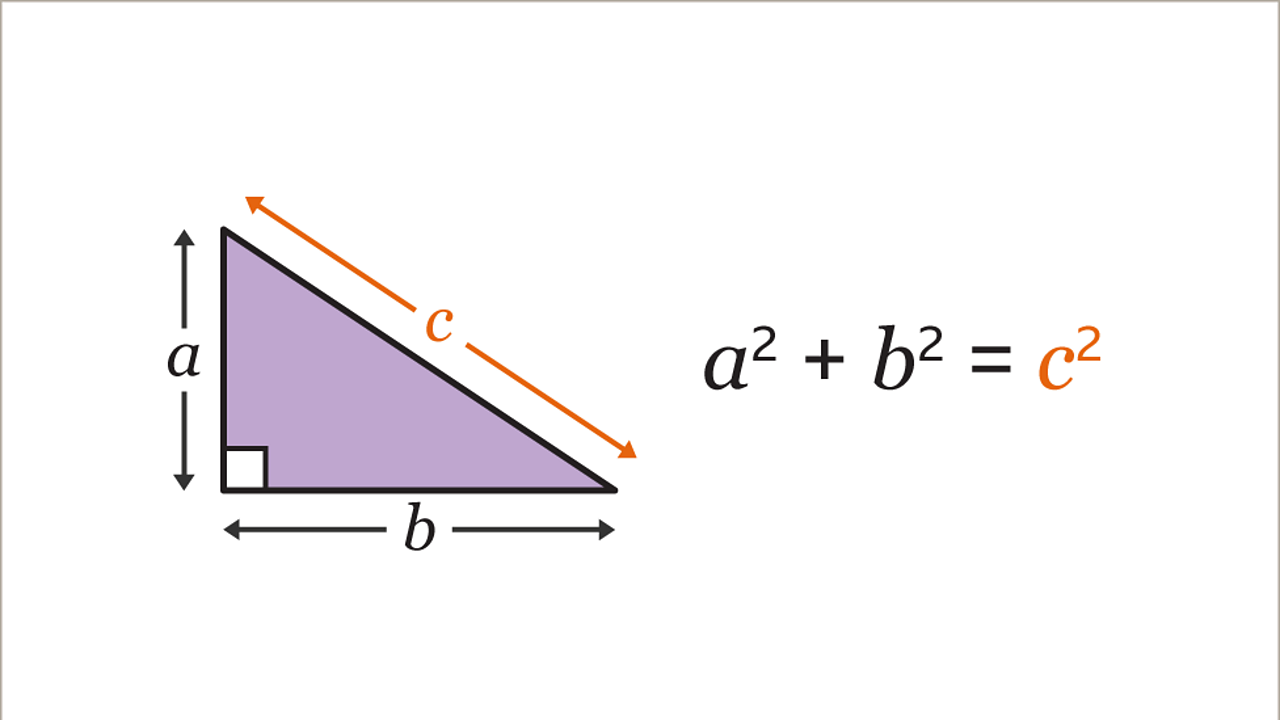
Circle Area
The area of a circle is determined using the formula A = πr²,
where "A" represents the area and "r" is the radius of
the circle. This concise formula elegantly captures the
essence of the circular expanse, revealing the space enclosed
by the circumference.
It's a straightforward mathematical
expression that transforms the radius into a powerful
determinant of the circle's two-dimensional region.